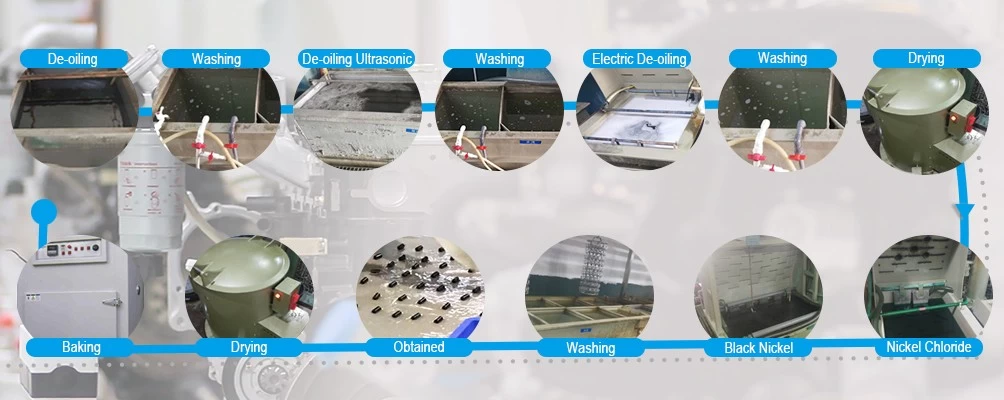
Analysis of the most common defects in zinc alloy die castings
June
www.xy-global.com
2022-03-28 18:38:55
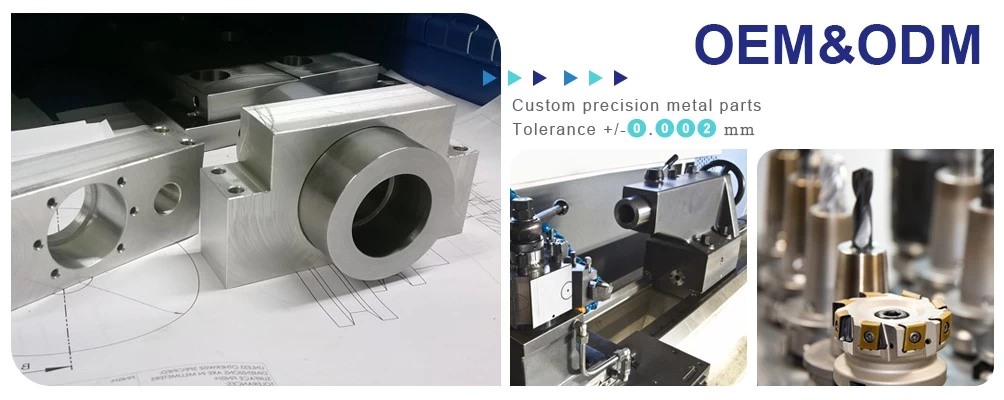
Zinc alloy die castings are currently widely used in various decorations, such as furniture accessories, architectural decoration, bathroom accessories, lighting parts, toys, tie clips, belt buckles, various metal buckles, etc., so the surface quality of the castings is relatively high. At the same time, good surface treatment performance is required. The most common defect of zinc alloy die castings is surface blistering.
Defect characterization: There are blisters on the surface of die-casting parts, which are found after die-casting, exposed after polishing or processing, and after oil spraying or electroplating. weil:
1. Caused by holes: mainly due to stomata and shrinkage mechanisms, stomata are often circular, while shrinkage is mostly irregular.
(1) Causes of pores: a. During the filling and solidification process of molten metal, holes are formed on the surface or inside of the casting due to the intrusion of gas. b The gas volatilized from the paint invades. c The gas content of the alloy liquid is too high, and it precipitates during solidification.
When the gas in the cavity, the gas volatilized from the paint, and the gas precipitated by the solidification of the alloy, when the mold exhaust is not good, the pores will eventually remain in the casting.
(2) Causes of shrinkage cavities: a) During the solidification process of molten metal, shrinkage cavities are generated due to the shrinkage of the volume or the lack of molten metal feeding at the final solidified part. B. The castings or castings with uneven thickness are overheated locally, resulting in slow solidification of a certain part, and a concave surface is formed on the surface when the volume shrinks. Due to the existence of pores and shrinkage cavities, when the die-casting parts are surface-treated, the holes may enter water. When baking after painting and electroplating, the gas in the holes will be heated and expanded; or the water in the holes will become steam and expand in volume. This results in blistering on the surface of the casting.
2. Intergranular corrosion caused by:
Harmful impurities in the composition of zinc alloys: lead, cadmium, and tin will gather at the grain boundaries to cause intergranular corrosion, and the metal matrix will be broken due to intergranular corrosion, and electroplating accelerates this scourge, and the parts affected by intergranular corrosion will expand and cause damage. The coating is lifted up, causing blistering on the surface of the casting. Especially in wet environments, intergranular corrosion can cause castings to deform, crack, and even shatter.
3. Cracks caused: water lines, cold separation lines, hot cracks.
Water lines and cold separation lines: During the filling process of the molten metal, the first molten metal contacting the mold wall solidifies prematurely, and the later molten metal cannot be fused with the solidified metal layer, forming a lamination on the surface of the casting. Stripe defects appear. The water marks are generally shallow on the surface of the casting; while the cold barrier may penetrate into the inside of the casting.
Hot crack: a When the thickness of the casting is uneven, the solidification process produces stress; b is ejected too early, and the metal strength is not enough; c, the force is uneven during ejection;
All of the above factors may cause cracks.
When there are water lines, cold separation lines and hot cracks in the die casting, the solution will penetrate into the cracks during electroplating, and will be converted into steam during baking, and the air pressure will lift the electroplating layer to form blisters.
Solution to defect:
Der Schlüssel zur Steuerung der Erzeugung von Poren besteht darin, die in das Gussgemisch gemischte Gasmenge zu reduzieren. Der ideale Metallstrom sollte kontinuierlich von der Düse beschleunigt werden, um den Hohlraum durch den Shunt-Kegel und den Läufer eindringen, um einen glatten und konsistenten Metallstrom zu bilden. Konische Läufer werden verwendet. Das Design, das heißt, der Gießfluss sollte mit einer Beschleunigungsrate allmählich von der Düse mit dem Ingat reduziert werden, kann diesen Zweck erreichen. In dem Füllsystem bildet das Mischgas auf Poren aufgrund turbulenter Strömung, gemischt mit der flüssigen Metallphase. Aus der Untersuchung des simulierten Druckgießverfahrens, in dem das geschmolzene Metall aus dem Gießsystem in den Hohlraum eintritt, ist es offensichtlich, dass der scharfe Übergang im Läufer und das inkrementelle Gießen der Querschnittsfläche des Läufers dazu führt Geschmolzenes Metall, um turbärig zu fließen und das Gas zu entsorgen, und das stabile geschmolzene Metall hilft dem Gas, der Überlaufnut und der Auslassnut aus dem Läufer und den Hohlraum eindringen und aus der Form ausgetragen werden.
Für den Schrumpfungshohlraum: Um alle Teile während des Verfestigungsprozesses des Druckgussteils gleichzeitig so viel wie möglich zu löschen, und vereinfachen gleichzeitig. Schrumpfhohlräume können durch angemessene Düsenkonstruktion, Gatestärke und Position, Formdesign, Formtemperatursteuerung und Kühlung vermieden werden. Für das intergranuläre Korrosionsphänomen: hauptsächlich den Inhalt schädlicher Verunreinigungen in Legierungsrohstoffen steuern, insbesondere der Blei <0.003%. Pay attention to the impurity elements brought by the waste.
Bei Wassermarkierungen und kalten Isolierungen kann die Formtemperatur erhöht werden, die Gatedrehzahl kann erhöht werden, oder die Überlaufnut kann im kalten Isolierbereich vergrößert werden, um das Erscheinungsbild der kalten Isolierung zu verringern.
Für heiße Risse: Ändern Sie nicht die Dicke des Druckgießens scharf, um Stress zu reduzieren; Passen Sie die relevanten Process-Prozessparameter an; Reduzieren Sie die Formtemperatur.