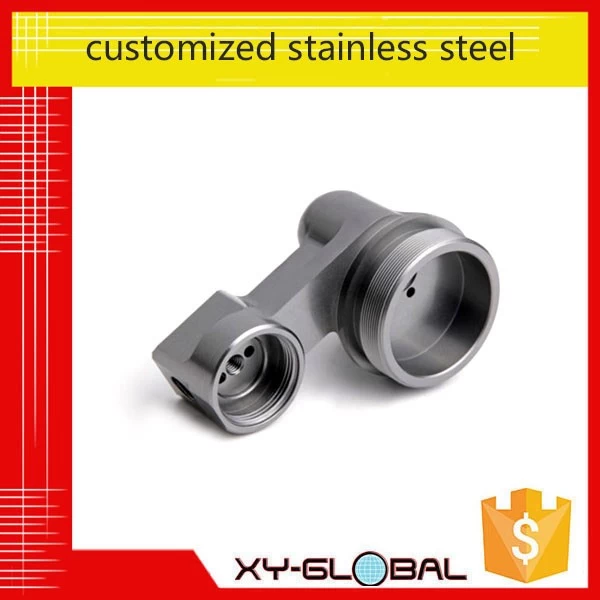
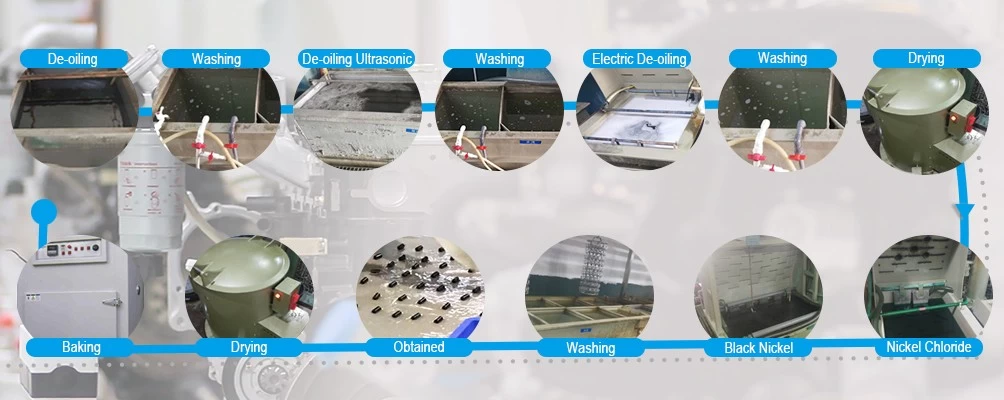
the processing of lost wax
Coolidge
www.diecastingpartsupplier.com
2018-08-10 09:23:18
Casts can be made of the wax model itself, the direct method, or of a wax copy of a model that need not be of wax, the indirect method. These are the steps for the indirect process:
1. Model-making. An artist or mould-maker creates an original model from wax, clay, or another material. Wax and oil-based clay are often preferred because these materials retain their softness.
2. Mouldmaking. A mould is made of the original model or sculpture. The rigid outer moulds contain the softer inner mould, which is the exact negative of the original model. Inner moulds are usually made of latex, polyurethane rubber or silicone, which is supported by the outer mould. The outer mould can be made from plaster, but can also be made of fiberglass or other materials. Most moulds are made of at least two pieces, and a shim with keys is placed between the parts during construction so that the mould can be put back together accurately. If there are long, thin pieces extending out of the model, they are often cut off of the original and moulded separately. Sometimes many moulds are needed to recreate the original model, especially for large models.
3. Wax. Once the mould is finished, molten wax is poured into it and swished around until an even coating, usually about ⁄8 inch (3 mm) thick, covers the inner surface of the mould. This is repeated until the desired thickness is reached. Another method is to fill the entire mould with molten wax and let it cool until a desired thickness has set on the surface of the mould. After this the rest of the wax is poured out again, the mould is turned upside down and the wax layer is left to cool and harden. With this method it is more difficult to control the overall thickness of the wax layer.
4. Removal of wax. This hollow wax copy of the original model is removed from the mould. The model-maker may reuse the mould to make multiple copies, limited only by the durability of the mould.
5. Chasing. Each hollow wax copy is then "chased": a heated metal tool is used to rub out the marks that show the parting line or flashing where the pieces of the mould came together. The wax is dressed to hide any imperfections. The wax now looks like the finished piece. Wax pieces that were moulded separately can now be heated and attached; foundries often use registration marks to indicate exactly where they go.
6. Spruing. The wax copy is sprued with a treelike structure of wax that will eventually provide paths for the molten casting material to flow and for air to escape. The carefully planned spruing usually begins at the top with a wax "cup," which is attached by wax cylinders to various points on the wax copy. The spruing does not have to be hollow, as it will be melted out later in the process.
7. Slurry. A sprued wax copy is dipped into a slurry of silica, then into a sand-like stucco, or dry crystalline silica of a controlled grain size. The slurry and grit combination is called ceramic shell mould material, although it is not literally made of ceramic. This shell is allowed to dry, and the process is repeated until at least a half-inch coating covers the entire piece. The bigger the piece, the thicker the shell needs to be. Only the inside of the cup is not coated, and the cup's flat top serves as the base upon which the piece stands during this process.
8. Burnout. The ceramic shell-coated piece is placed cup-down in a kiln, whose heat hardens the silica coatings into a shell, and the wax melts and runs out. The melted wax can be recovered and reused, although it is often simply burned up. Now all that remains of the original artwork is the negative space formerly occupied by the wax, inside the hardened ceramic shell. The feeder, vent tubes and cup are also now hollow.
9. Testing. The ceramic shell is allowed to cool, then is tested to see if water will flow freely through the feeder and vent tubes. Cracks or leaks can be patched with thick refractory paste.

1. Model-making. An artist or mould-maker creates an original model from wax, clay, or another material. Wax and oil-based clay are often preferred because these materials retain their softness.
2. Mouldmaking. A mould is made of the original model or sculpture. The rigid outer moulds contain the softer inner mould, which is the exact negative of the original model. Inner moulds are usually made of latex, polyurethane rubber or silicone, which is supported by the outer mould. The outer mould can be made from plaster, but can also be made of fiberglass or other materials. Most moulds are made of at least two pieces, and a shim with keys is placed between the parts during construction so that the mould can be put back together accurately. If there are long, thin pieces extending out of the model, they are often cut off of the original and moulded separately. Sometimes many moulds are needed to recreate the original model, especially for large models.
3. Wax. Once the mould is finished, molten wax is poured into it and swished around until an even coating, usually about ⁄8 inch (3 mm) thick, covers the inner surface of the mould. This is repeated until the desired thickness is reached. Another method is to fill the entire mould with molten wax and let it cool until a desired thickness has set on the surface of the mould. After this the rest of the wax is poured out again, the mould is turned upside down and the wax layer is left to cool and harden. With this method it is more difficult to control the overall thickness of the wax layer.
4. Removal of wax. This hollow wax copy of the original model is removed from the mould. The model-maker may reuse the mould to make multiple copies, limited only by the durability of the mould.
5. Chasing. Each hollow wax copy is then "chased": a heated metal tool is used to rub out the marks that show the parting line or flashing where the pieces of the mould came together. The wax is dressed to hide any imperfections. The wax now looks like the finished piece. Wax pieces that were moulded separately can now be heated and attached; foundries often use registration marks to indicate exactly where they go.
6. Spruing. The wax copy is sprued with a treelike structure of wax that will eventually provide paths for the molten casting material to flow and for air to escape. The carefully planned spruing usually begins at the top with a wax "cup," which is attached by wax cylinders to various points on the wax copy. The spruing does not have to be hollow, as it will be melted out later in the process.
7. Slurry. A sprued wax copy is dipped into a slurry of silica, then into a sand-like stucco, or dry crystalline silica of a controlled grain size. The slurry and grit combination is called ceramic shell mould material, although it is not literally made of ceramic. This shell is allowed to dry, and the process is repeated until at least a half-inch coating covers the entire piece. The bigger the piece, the thicker the shell needs to be. Only the inside of the cup is not coated, and the cup's flat top serves as the base upon which the piece stands during this process.
8. Burnout. The ceramic shell-coated piece is placed cup-down in a kiln, whose heat hardens the silica coatings into a shell, and the wax melts and runs out. The melted wax can be recovered and reused, although it is often simply burned up. Now all that remains of the original artwork is the negative space formerly occupied by the wax, inside the hardened ceramic shell. The feeder, vent tubes and cup are also now hollow.
9. Testing. The ceramic shell is allowed to cool, then is tested to see if water will flow freely through the feeder and vent tubes. Cracks or leaks can be patched with thick refractory paste.